
- Shandong Loyal Industrial Co.,Ltd.
- Macaroni Production Machine Instant Noodle Machine Biscuit Making Machine
Home> Company News> The Ultimate Guide to Conveyor Microwave Ovens in 2024

The Ultimate Guide to Conveyor Microwave Ovens in 2024
2024-04-29 15:28:25Introduction
Welcome to The Ultimate Guide to Conveyor Microwave Ovens in 2024. In this comprehensive guide, we delve into the revolutionary advancements and applications of conveyor microwave ovens in the realm of food preparation and industrial processes. From their inception to their current state-of-the-art capabilities, we explore how these innovative appliances are shaping the landscape of microwave technology and redefining efficiency in various sectors. Let's embark on a journey to uncover the transformative potential of conveyor microwave ovens.

How Conveyor Microwaves Work
Conveyor microwaves are the epitome of technological advancement in the world of cooking, with their underlying principles deeply rooted in electromagnetic waves and heat transfer mechanisms. Unlike conventional ovens that rely primarily on conduction of heat, these ingenious appliances use microwave radiation to penetrate food, causing molecular agitation and generating heat from within. At the heart of its operation is the magnetron, a device responsible for generating high-frequency microwaves. These microwaves are then directed through a waveguide system to the cooking chamber where they interact with the water molecules in the food. As microwaves oscillate at frequencies ranging from 2.45 to 5.8 gigahertz, they cause polar molecules such as water, fats, and sugars to rotate rapidly, generating heat through friction. The conveyor system is an integral component of these ovens, ensuring that food is evenly exposed to microwave radiation. Food placed on the conveyor is subjected to a continuous stream of microwaves as it passes through the cooking chamber. This continuous motion not only facilitates even heating, but also increases the efficiency of the cooking process, allowing for precise control of cooking time and temperature. Essentially, the working principle of a conveyor microwave oven revolves around the efficient conversion of electromagnetic energy into heat energy within a controlled cooking environment. By harnessing the power of microwaves and using innovative delivery technology, these ovens offer a convenient and effective solution for achieving consistent cooking results in a variety of cooking applications.
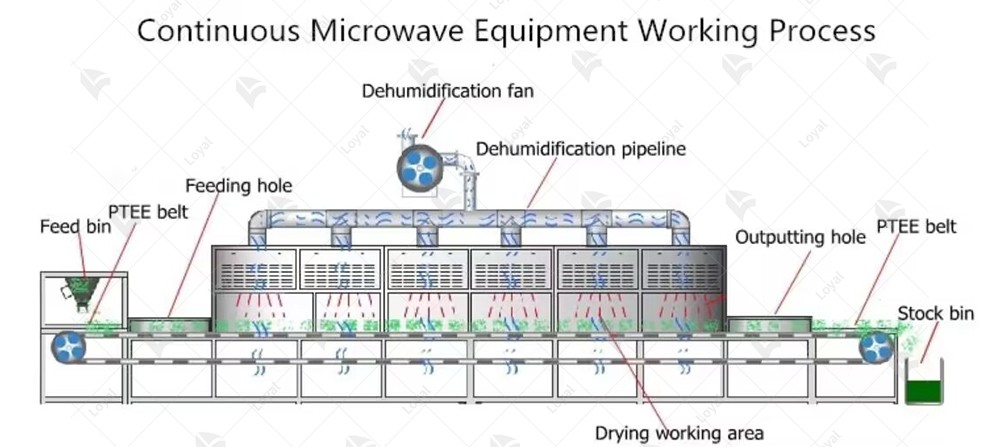
Advantages of conveyor microwave ovens
|
Advantages |
Description |
|
Faster Cooking |
Conveyor microwave ovens utilize a continuous conveyor belt system, allowing for rapid and consistent cooking of food products. The microwave energy quickly heats the food as it moves along the conveyor, resulting in shorter cooking times compared to conventional ovens. This is particularly advantageous in high-volume food production settings where efficiency is paramount. |
|
Uniform Heating |
One of the key advantages of conveyor microwave ovens is their ability to provide uniform heating throughout the food product. Unlike conventional ovens where heating may be uneven, microwave energy penetrates the food evenly, ensuring consistent cooking from edge to edge. This uniform heating helps to maintain food quality and prevents overcooking or undercooking of individual portions. |
|
Energy Efficiency |
Conveyor microwave ovens are known for their energy efficiency, as they use microwave energy to directly heat the food rather than heating the surrounding air. This results in minimal energy wastage and lower operating costs compared to traditional cooking methods. Additionally, the rapid cooking times of conveyor microwave ovens further contribute to energy savings, making them an environmentally friendly option for food processing facilities. |
|
Space Savings |
In commercial kitchens and food production facilities where space is at a premium, conveyor microwave ovens offer a space-saving solution. Their compact design and conveyor belt system allow for efficient use of kitchen space, maximizing production capacity without the need for additional cooking equipment. This is especially beneficial for businesses looking to optimize their kitchen layout and streamline workflow. |
|
Versatility |
Conveyor microwave ovens are highly versatile and can be used to cook a wide range of food products, including meats, vegetables, baked goods, and ready-to-eat meals. They offer flexibility in cooking methods, allowing for steaming, roasting, baking, and reheating, all within the same appliance. This versatility makes conveyor microwave ovens ideal for diverse food service operations, from fast-food restaurants to catering businesses. |

Key components of conveyor microwave ovens
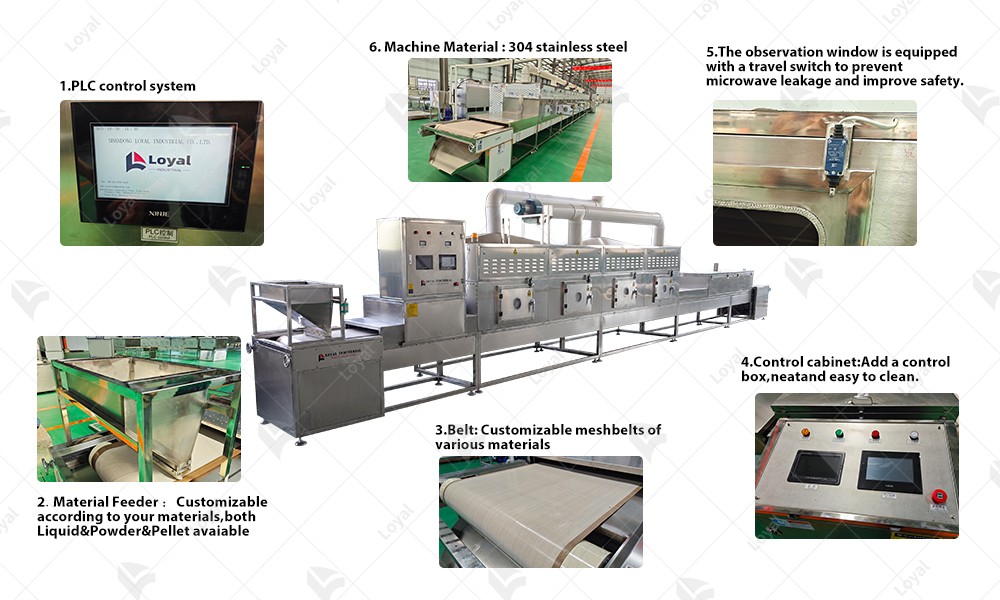
1. Magnetron: The heart of the microwave oven, the magnetron generates the electromagnetic waves required for heating food. It converts electrical energy into microwave radiation, which is then directed into the oven cavity.
2. Waveguide: Responsible for directing the microwave radiation from the magnetron into the oven cavity, the waveguide ensures efficient transmission of electromagnetic waves without significant loss of energy.
3. Conveyor Belt: Unlike traditional microwave ovens with a stationary platform, conveyor microwave ovens feature a conveyor belt that moves food items through the cooking chamber. This allows for continuous and automated cooking, making them ideal for high-volume food production settings.
4. Cavity: The cavity is the enclosed space within the microwave oven where the food is placed for cooking. It is designed to reflect and distribute the microwave radiation evenly, ensuring uniform heating of the food items.
5. Control Panel: The control panel houses the interface through which users can set the cooking parameters such as time, temperature, and power level. It also displays important information such as cooking progress and error messages.
6. Cooling System: To prevent overheating and ensure safe operation, conveyor microwave ovens are equipped with a cooling system. This may include fans, vents, and heat sinks to dissipate excess heat generated during operation.

Technical parameters
|
Technical Parameters Of Continuous Microwave Dryer Industrial Microwave Drying Machine |
|||||
|
Model |
Size LWH(Can be customized according |
Output |
Dewaterability |
Sterilization |
Baking and Roasting capacity |
|
LY-10KW |
5000mm825mm1750mm |
≥10KW |
10KG/Hour |
100KG/Hour |
30-50KG/Hour |
|
LY-20KW |
8000mm825mm1750mm |
≥20KW |
20KG/Hour |
200KG/Hour |
60-100KG/Hour |
|
LY-30KW |
8500mm1160mm1750mm |
≥30KW |
30KG/Hour |
300KG/Hour |
90-150 KG/Hour |
|
LY-40KW |
10000mm1160mm1750mm |
≥40KW |
40KG/Hour |
40KG/Hour |
120-200KG/Hour |
|
LY-50KW |
12500mm1160mm1750mm |
≥50KW |
50KG/Hour |
500KG/Hour |
150-250KG/Hour |
|
LY-60KW |
13500mm1450mm1750mm |
≥60KW |
60KG/Hour |
600KG/Hour |
180-300KG/Hour |
|
LY-70KW |
13500mm1500mm1750mm |
≥70KW |
70KG/Hour |
700KG/Hour |
210-350KG/Hour |
|
LY-80KW |
13500mm1650mm1750mm |
≥80KW |
80KG/Hour |
800KG/Hour |
240-400KG/Hour |
|
LY-100KW |
16800mm1650mm1750mm |
≥100KW |
100KG/Hour |
1000KG/Hour |
300-500KG/Hour |
|
LY-150KW |
22400mm1850mm1750mm |
≥150KW |
150KG/Hour |
1500KG/Hour |
450-750KG/Hour |
|
LY-200KW |
27000mm1850mm1750mm |
≥250KW |
250KG/Hour |
2500KG/Hour |
750-1250/Hour |
|
LY-300KW |
32000mm1850mm1750mm |
≥300KW |
300KG/Hour |
3000KG/Hour |
900-1500KG/Hour |
|
Power Supply |
380V±10% 50Hz±1% Three-Phase Five-Wire |
||||
|
Microwave Output Frequency |
2450±50Mhz |
||||
|
Microwave Input Apparent Power |
≤168Kva |
||||
|
Microwave Output Power |
≥120Kw |
||||
|
Microwave Power Adjustment Range |
0-30Kw(Adjustable) |
||||
|
Ambient Temperature |
-5-40°C |
||||
|
Relative Humidity |
≤80%, Surrounding Environment:No Corrosive Gas, Conductive Dust And Explosive Gas |
||||
|
Transmission Speed |
0-10m/Min(Adjustable) |
||||

Applications of Conveyor Microwave Ovens
Food Industry Applications
In the food industry, conveyor microwave ovens are indispensable tools for enhancing productivity while maintaining quality. These ovens are extensively used for cooking, baking, and heating various food products, ranging from baked goods to ready-to-eat meals. The controlled heating mechanism of conveyor microwave ovens ensures uniform cooking, resulting in consistent taste and texture. Moreover, their rapid heating capability significantly reduces processing time, allowing food manufacturers to meet the demands of fast-paced markets without compromising on quality.
Industrial Processing
Beyond the realm of food, conveyor microwave ovens find applications in industrial processing. From drying and curing to sterilization, these ovens play a vital role in optimizing production processes across diverse sectors such as pharmaceuticals, textiles, and ceramics. The precise temperature control and rapid heating capabilities of conveyor microwave ovens enable manufacturers to achieve desired results efficiently, thereby streamlining operations and minimizing downtime.
Research and Development
In research and development laboratories, conveyor microwave ovens serve as indispensable tools for experimentation and innovation. Scientists and engineers leverage the unique heating properties of microwaves to explore novel applications in materials science, chemistry, and biotechnology. These ovens facilitate precise control over heating parameters, allowing researchers to conduct experiments with unprecedented accuracy and reproducibility. Whether synthesizing new compounds or studying the behavior of materials under specific conditions, conveyor microwave ovens offer unparalleled versatility and reliability.
Environmental Sustainability
Conveyor microwave ovens also contribute to environmental sustainability efforts by promoting energy efficiency and reducing waste. Compared to conventional heating methods, such as gas and electric ovens, microwave technology consumes significantly less energy and produces fewer greenhouse gas emissions. Additionally, the rapid heating and uniform cooking capabilities of conveyor microwave ovens minimize food wastage by ensuring optimal utilization of resources. As businesses increasingly prioritize sustainability initiatives, the adoption of conveyor microwave ovens emerges as a strategic choice to minimize environmental impact while maximizing operational efficiency.
In conclusion, conveyor microwave ovens represent a pinnacle of technological innovation with diverse applications across industries. From enhancing productivity in food manufacturing to enabling breakthroughs in research and development, these appliances continue to redefine the way we cook, process, and innovate. As we look towards the future, the integration of conveyor microwave ovens into various sectors promises to drive efficiency, sustainability, and progress in 2024 and beyond.

Technological progress and innovation of conveyor microwave ovens
In 2024, the landscape of microwave technology continues to evolve, with conveyor microwave ovens leading the charge in revolutionizing food processing and cooking industries. These cutting-edge appliances integrate the principles of traditional microwave ovens with the efficiency of conveyor systems, offering unparalleled speed, consistency, and quality in food preparation.
Conveyor microwave ovens leverage advanced electromagnetic waves to rapidly and evenly cook food items as they pass through the conveyor belt. This innovative technology ensures precise control over the cooking process, resulting in uniform heating and optimal texture retention across a wide range of food products.
One of the key advantages of conveyor microwave ovens is their ability to streamline production processes in commercial kitchens and food manufacturing facilities. By automating the cooking process and reducing manual labor requirements, these ovens significantly enhance operational efficiency and productivity, ultimately translating into cost savings for businesses.
Furthermore, conveyor microwave ovens are renowned for their versatility and adaptability, capable of handling various types of food products, including baked goods, meats, vegetables, and ready-to-eat meals. Their customizable settings and adjustable conveyor speeds allow chefs and food manufacturers to tailor the cooking parameters according to specific recipes and production requirements.
Moreover, conveyor microwave ovens prioritize food safety by employing advanced features such as temperature monitoring, moisture control, and sanitation protocols. These built-in safeguards mitigate the risk of foodborne illnesses and ensure compliance with regulatory standards, reinforcing consumer confidence in the quality and safety of processed foods.
As technological advancements continue to drive innovation in the culinary world, conveyor microwave ovens stand at the forefront of the revolution, reshaping the way we perceive and approach food preparation. With their unmatched efficiency, precision, and versatility, these appliances are set to redefine the standards of excellence in the food industry for years to come.

Challenges and Limitations of Conveyor Microwave Ovens
Conveyor microwave ovens have emerged as a groundbreaking solution in the food industry, promising efficient and uniform heating processes. However, despite their numerous advantages, these innovative appliances are not without their challenges and limitations.
1. Heating Uniformity
One of the primary challenges associated with conveyor microwave ovens is ensuring uniform heating throughout the food product. While microwave technology facilitates rapid and consistent heating, variations in product size, shape, and composition can lead to uneven heating patterns. Addressing this issue requires meticulous calibration of microwave power levels and conveyor speed to achieve optimal results across different food types.
2. Moisture Content Control
Maintaining the desired moisture content in food products presents another significant challenge for conveyor microwave ovens. The intense heat generated by microwaves can quickly evaporate moisture, resulting in dry or overcooked food items. Achieving precise control over moisture levels demands sophisticated sensor technology and precise modulation of microwave power to prevent undesirable texture and flavor changes.
3. Product Quality Preservation
While conveyor microwave ovens offer unparalleled speed and efficiency, preserving the quality attributes of food products remains a critical concern. High temperatures and rapid heating rates can trigger chemical reactions and structural changes that compromise taste, texture, and nutritional value. Mitigating these effects requires a delicate balance between microwave power, exposure time, and advanced food processing techniques to ensure optimal product quality.
4. Energy Consumption
Conveyor microwave ovens are renowned for their energy efficiency compared to traditional cooking methods. However, optimizing energy consumption while maintaining performance levels poses a continuous challenge. Innovations in microwave technology, such as variable power settings and advanced insulation materials, are instrumental in reducing energy waste and enhancing overall operational sustainability.
5. Regulatory Compliance
Meeting stringent regulatory standards and food safety regulations is imperative for the widespread adoption of conveyor microwave ovens. Ensuring compliance with established guidelines requires comprehensive testing and validation procedures to guarantee the elimination of potential health risks, such as uneven heating or inadequate pathogen control. Collaborative efforts between industry stakeholders and regulatory authorities are essential to establish and enforce rigorous standards for microwave food processing.

Post-maintenance of conveyor microwave ovens
After the installation and initial operation of conveyor microwave ovens, ensuring proper maintenance is paramount to sustain optimal performance and longevity. Here's a comprehensive guide on post-maintenance procedures for conveyor microwave ovens in 2024.
1. Regular Inspection and Cleaning: Scheduled inspections are essential to identify any potential issues early on. Inspect conveyor belts, magnetrons, waveguides, and cooling systems for signs of wear, damage, or malfunction. Regular cleaning of the interior and exterior components helps prevent the buildup of food residues and ensures efficient operation.
2. Functional Testing: Conduct routine functional tests to verify that all components are operating within specified parameters. This includes checking power levels, temperature settings, and conveyor speed. Any deviations should be promptly addressed to avoid performance degradation.
3. Calibration and Adjustment: Calibration of sensors and controls is crucial for accurate cooking performance. Periodically calibrate power levels, temperature sensors, and conveyor speed to maintain consistency in cooking results. Additionally, adjust settings as necessary to accommodate changes in food product specifications or production requirements.
4. Safety Checks: Safety should always be a top priority when operating conveyor microwave ovens. Regularly inspect safety interlocks, door seals, and emergency stop mechanisms to ensure they are functioning correctly. Address any safety concerns immediately to mitigate risks of accidents or injuries.
5. Component Replacement: Over time, certain components may wear out or deteriorate, impacting the efficiency and reliability of the oven. Replace worn-out conveyor belts, damaged magnetrons, or faulty control panels as needed to prevent downtime and maintain productivity.
6. Upgrades and Modifications: Stay informed about advancements in conveyor microwave oven technology and consider implementing upgrades or modifications to enhance performance and energy efficiency. This may include installing new heating elements, upgrading control systems, or integrating automation features for increased productivity.
7. Documentation and Record-Keeping: Maintain detailed records of all maintenance activities, including inspections, repairs, and upgrades. Documenting these procedures facilitates traceability and allows for informed decision-making regarding future maintenance needs.
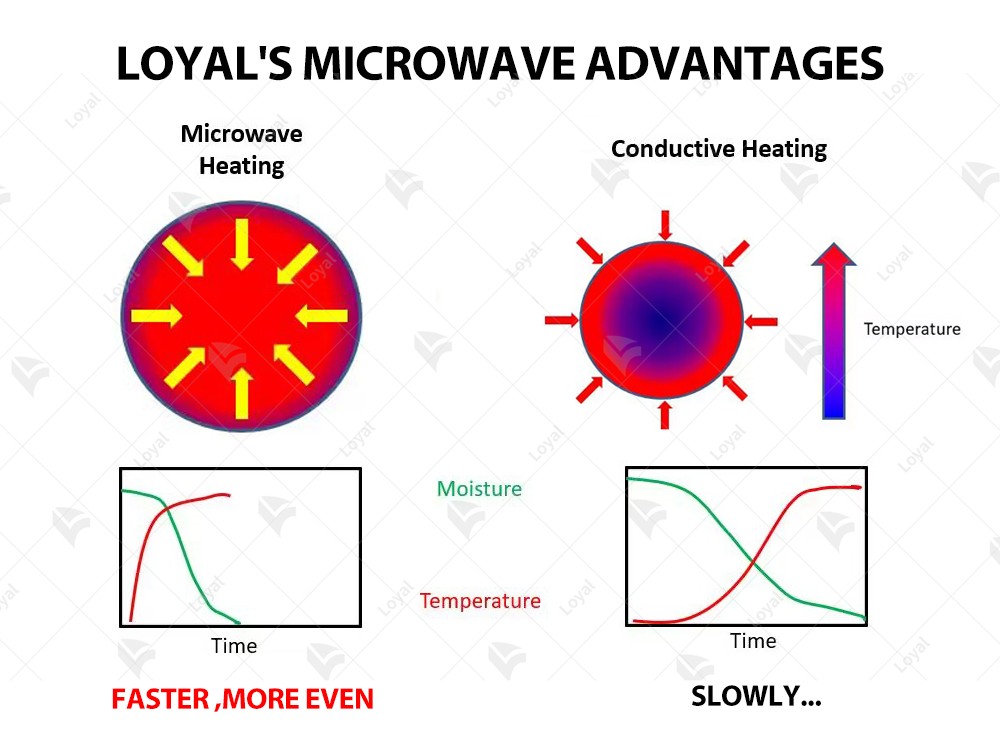
References
The following are five authoritative foreign literature websites in the field of industrial microwaves:
1. IEEE Xplore Digital Library
Website: [https://ieeexplore.ieee.org/]
2.ScienceDirect
Website: [https://www.sciencedirect.com/]
3. SpringerLink
Website: [https://link.springer.com/]
4. Wiley Online Library
Website: [https://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/]
5. PubMed
Website: [https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/]
 Commercial Japanese Panko Bread Crumb Grinder Machine
Commercial Japanese Panko Bread Crumb Grinder Machine Japanese Bread Crumbs Processing Line
Japanese Bread Crumbs Processing Line Automatic Cookies Making Machines
Automatic Cookies Making Machines Fully Automatic Biscuit Making Machines
Fully Automatic Biscuit Making Machines